Table of Contents
Imagine discovering that the secret to Florida’s thriving termite colonies lies with an almost mythical figure—the termite queen. This extraordinary insect can lay thousands of eggs daily, ensuring her colony’s survival and expansion. Understanding the role of termite queens can help you better protect your home from these relentless invaders.
Key Takeaways
- Role and Importance of Termite Queens: Termite queens are central to the colony’s survival and expansion in Parrish, FL, capable of laying thousands of eggs daily.
- Identifying Termite Queens: Recognize termite queens by their immense size (1.5 to 2 inches long) and swollen abdomens, which are essential for high egg production.
- Pheromonal Influence: The queen’s pheromones regulate colony activities, making her removal crucial for effective termite control.
- Secondary and Tertiary Reproductives: In the queen’s absence, secondary and tertiary reproductives can take over egg production, ensuring the colony’s survival.
- Lifespan and Impact: A queen termite can live up to 25 years, contributing to significant infestations over time.
- Effective Control Strategies: Identifying and targeting termite queens and their pheromones using bait systems can disrupt and control termite colonies effectively.
What Do Subterranean Termite Queens And Reproductives Look Like?

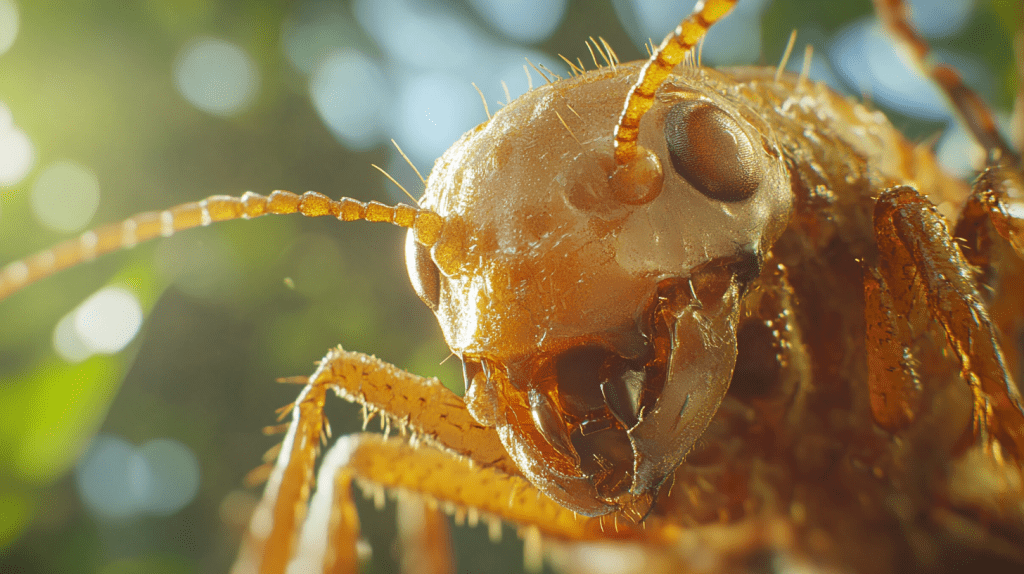
Subterranean termite queens differ significantly from workers and soldiers in appearance. Queens, who are vital for their egg-laying capabilities, stand out due to their large size and distinct features.
Identifying Termite Queens
Termite queens exhibit an intensified growth compared to other colony members. Typically, they measure about 1.5 to 2 inches long. Their abdomens expand immensely to maximize egg production, making them appear swollen. Often, you’ll see their color range from pale brown to dark brown.
Size and Appearance
When compared to workers, termite queens are giants. The workers usually measure about 1/8 of an inch, so the queen’s elongated body is unmistakable in the nest. Their extended abdomen houses reproductive organs, contributing to the continual birth of new termites. This trait establishes the queen’s role distinctly within the colony structure in Parrish, FL.
Subterranean Termite Identification

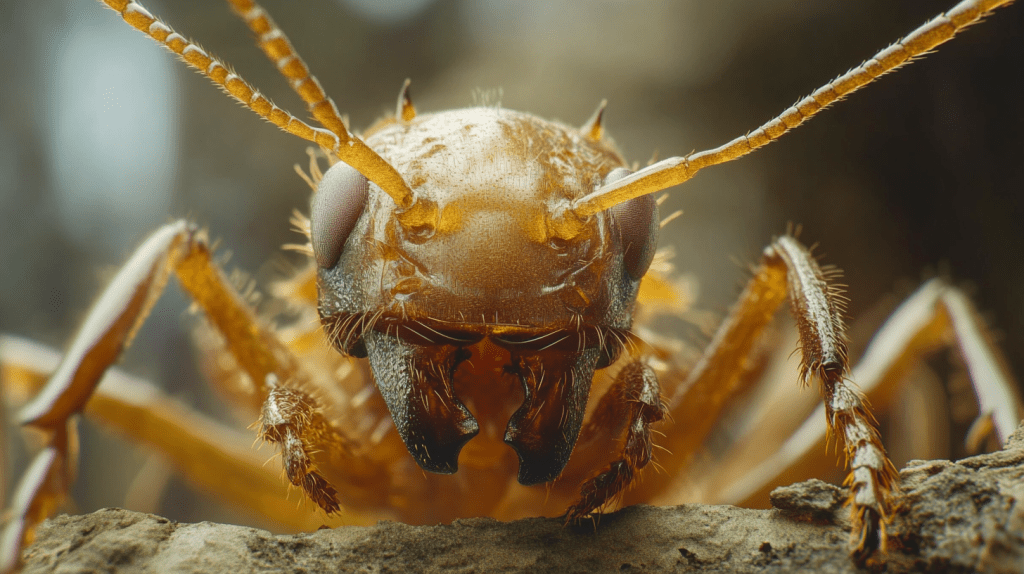
Scientific Family: Rhinotermitidae
Color: Varies from creamy white to dark brown or black.
Size: Approximately ⅛ inch in length.
Number of Legs: Six
Antennae: Present
Body Shape: Long, narrow, and oval-shaped.
Region Found: Distributed throughout the United States.
Reproductives’ Characteristics
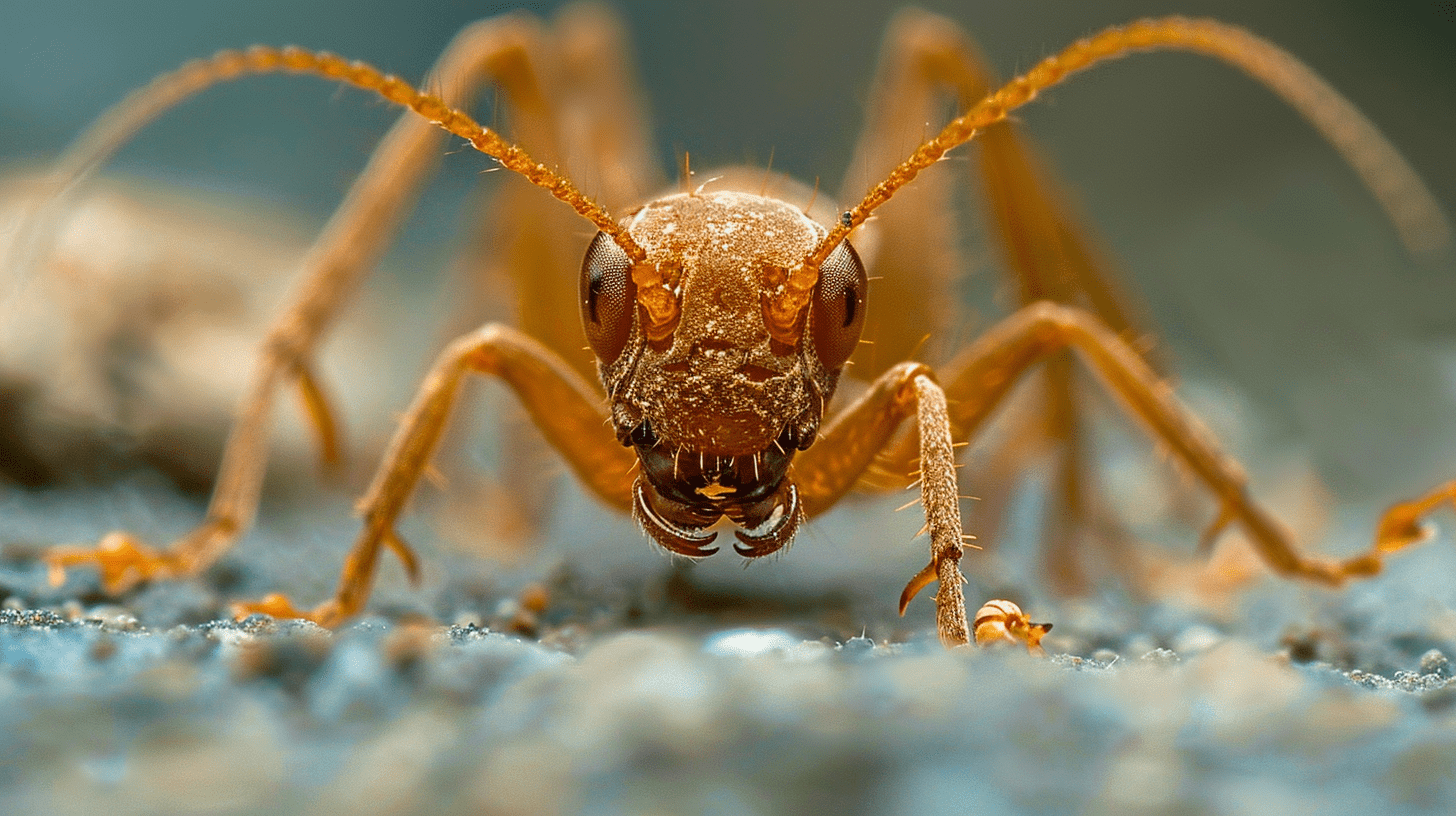
Alongside the queen, reproductives, including kings, play crucial roles. Kings are slightly larger than workers but much smaller than the queen. They possess wings during their swarming phase which they shed after mating. Reproductives have darker bodies and prominent wing scars on their backs after they lose their wings.

Expert Pest Control in Parrish!
Ready to keep your home pest-free? Reach out to Parrish Pest Control at (941) 297-2817 for fast and effective pest management solutions. Serving Parrish, FL, we guarantee a safe, comfortable, and pest-free environment for your home.
Get StartedDistinguishing Features
Several distinguishing features help in identifying a termite queen. Apart from size, their unique pheromones set them apart. These chemicals regulate colony activities and reproduction rates. Their pheromonal influence maintains social harmony within the subterranean community.
Understanding these distinguishing features aids in termite queen control strategies. Recognizing the queen and reproductives supports effective termite queen removal and overall pest management efforts within Parrish, FL, protecting local homes from potential termite infestations.
Role Of The Queen
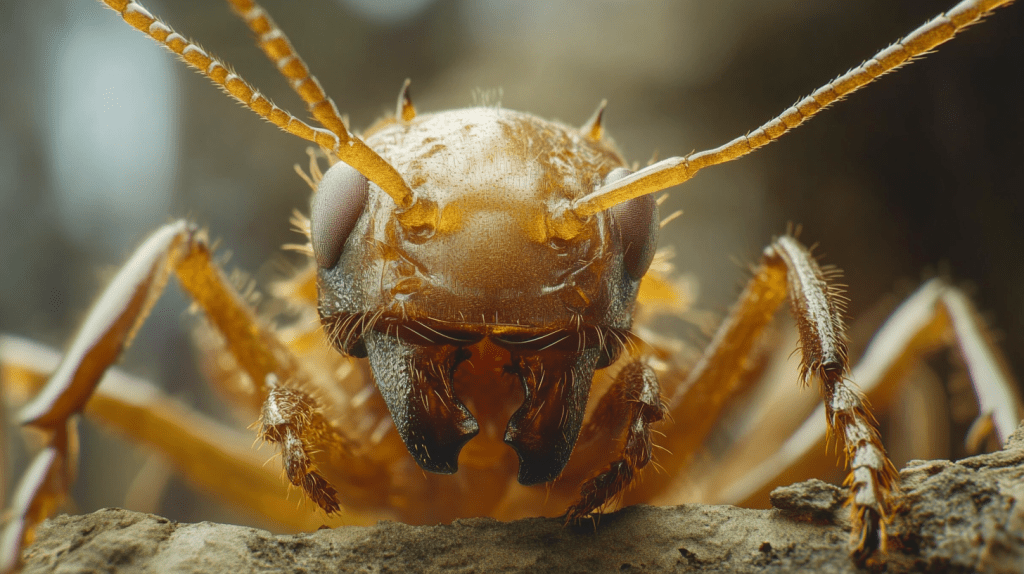

The termite queen plays an indispensable role in the termite colony’s lifecycle. In Parrish, FL, where the climate is ideal for termites, understanding her role helps grasp why termite control is crucial. The queen’s primary function is reproduction. She lays thousands of eggs daily, ensuring the colony’s continuous growth and survival. Her ability to produce such a massive number of eggs defines her as the central figure in the colony.
You’ll find the queen’s physical traits fascinating. Her swollen abdomen, which can reach up to 2 inches long, maximizes her egg-laying capacity. This distinctive size and shape differentiate her from other termites, like workers and kings. Identifying the termite queen becomes easier when you look for these physical markers. Recognizing her is the first step in effective termite control.
The termite queen’s pheromones govern the colony’s activities. These chemicals communicate exact tasks, from feeding larvae to foraging for food. Her pheromones ensure the colony functions like a well-oiled machine. If disrupting the colony is your goal, eliminating the queen is essential, as her pheromones hold everything together.
In the context of termite control, the queen’s presence poses a important challenge. Her prolific egg production leads to large infestations, making termite queen removal a top priority in pest management strategies. Understanding how to kill the termite queen effectively can prevent future infestations. This knowledge is especially critical in Parrish, FL, where termite problems persist due to the favorable climate.
Finally, the relationship between the termite queen and other colony members underscores her importance. The termite queen vs. worker comparison highlights her unique role. While workers maintain and protect the colony, the queen ensures its future by reproducing. This ever-changing interaction makes the termite queen a pivotal figure in the colony’s lifecycle, stressing why professional termite control methods focus on her elimination.
Primary Reproductives
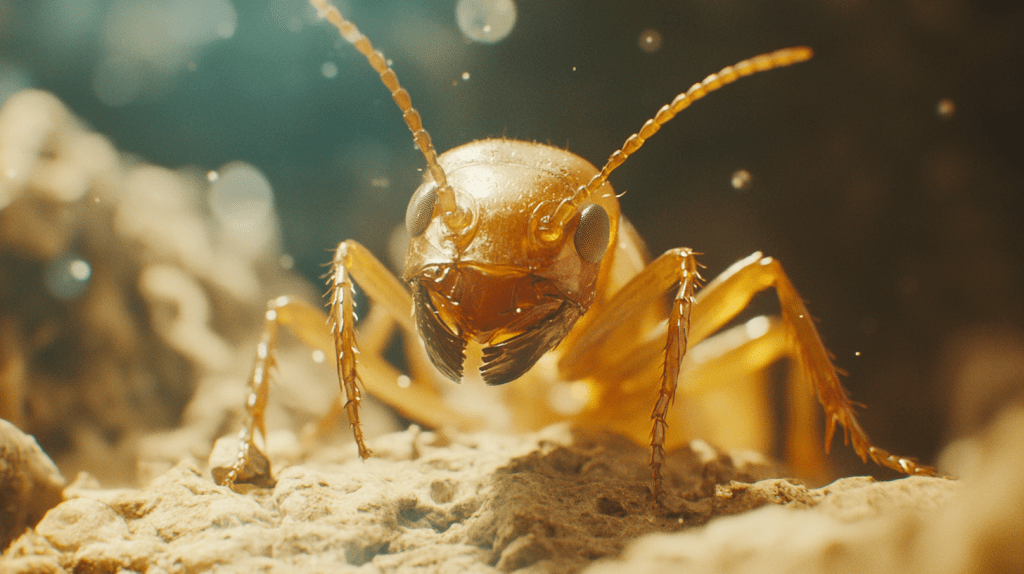

Termite queens, the primary reproductives, take center stage in termite colonies. These queens, alongside kings, ensure the colony’s expansion and survival. Especially in places like Parrish, FL, understanding their role helps design effective termite control strategies.
Queen’s Role in Reproduction
The termite queen’s primary role is reproduction. She can lay thousands of eggs daily, ensuring the colony’s growth. Her size, ranging between 1.5 to 2 inches due to her swollen abdomen, reflects her egg-laying capacity. This immense reproductive ability makes termite queen removal essential in controlling infestations. Without the queen, the colony’s ability to regenerate vanishes.
Pheromones and Colony Regulation
Unique pheromones produced by the queen help regulate colony activities. These chemical signals ensure smooth coordination among workers, soldiers, and other colony members. If you eliminate the termite queen, these pheromones cease, leading to disorganization within the colony. For those in Parrish, FL, targeting the pheromones can provide an effective strategy to manage termites.
Lifespan and Impact on Infestations
A termite queen’s lifespan can reach up to 25 years. During this period, the queen contributes to important infestations if uncontrolled. The longevity and prolific egg-laying create large colonies, which can damage wooden structures rapidly. So, understanding how to kill termite queens is vital for long-term termite control.
Relationship with the King
The termite king plays a supportive role, mating with the queen to ensure continual egg production. This partnership is crucial for the colony’s sustainability. In Parrish, FL’s favorable climate, this relationship often results in rapid colony expansion. Termite queen and king dynamics, hence, directly influence the infestation level in homes and buildings.
Identifying and Removing Termite Queens
Identifying the termite queen in a colony is the first step in effective termite queen control. The queen’s distinct size and location within the nest make her identifiable. Termite queen treatment focuses on reaching and eliminating her to cease reproduction. Techniques include baiting systems designed to target queens, ensuring their demise, and preventing the colony from thriving.
Understanding the biological, agricultural, and environmental relationships of termite queens can help you in making informed decisions about protecting your property. Effective termite queen strategies, from identifying to eliminating, are key components in managing infestations successfully.
Secondary And Tertiary Reproductives
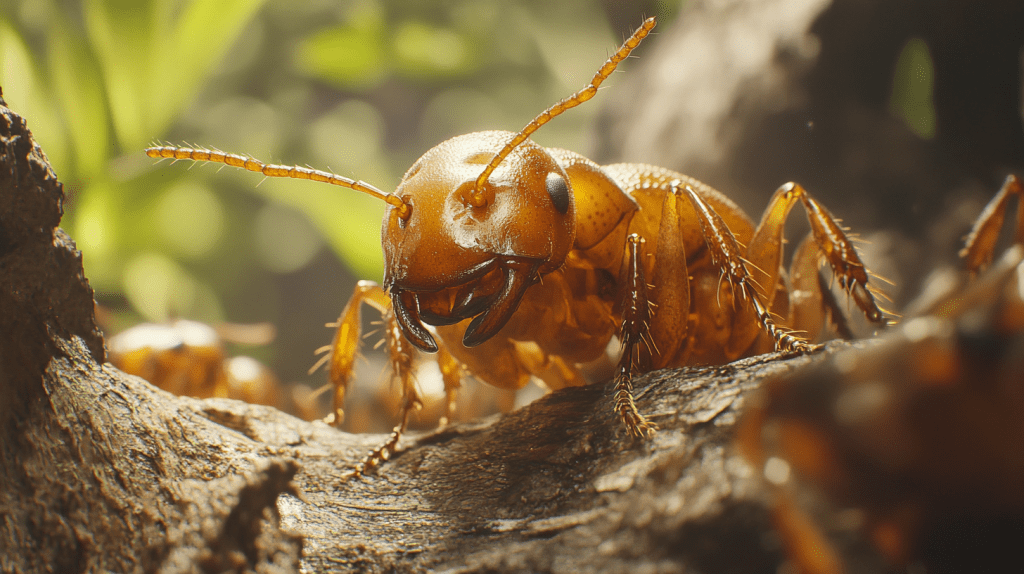
Secondary and tertiary reproductives play critical roles in termite colonies, especially in regions like Parrish, FL, where termite activity peaks due to ideal climates. Understanding these roles enhances your knowledge of termite queens and their colonies.
Functions and Importance
Secondary and tertiary reproductives become crucial when the primary termite queen can’t fulfill her role due to damage or death. These reproductives rapidly step in to ensure colony growth doesn’t halt. With their capacity to produce eggs, they maintain colony numbers when needed the most. If you aim to eliminate termite queens, it’s vital to acknowledge these backup players, as they can sustain the colony in her absence.
Identifying Characteristics
Secondary reproductives often resemble workers but possess slightly larger sizes and functional reproductive organs. Tertiary reproductives look like nymphs with wing buds or underdeveloped wings. Recognizing these reproducibles is essential in comprehensive termite queen control efforts, particularly when dealing with termite infestations that spread across large areas.
Pheromone Influence
The primary termite queen’s pheromones inhibit secondary and tertiary reproductives from becoming active. But, if her influence wanes, these backup reproductives ramp up egg production. This adaptive mechanism in termites underscores the complexity of their social structure and reproductive strategies. Addressing termite queen removal effectively, you must consider the potential for these alternate reproductives to take over.
Environmental Impact
In Parrish, FL, where termites thrive, understanding the existence and impact of secondary and tertiary reproductives is pivotal for successful termite control. Their ability to keep the colony going even after the primary queen’s removal challenges conventional pest control methods. So, deploying comprehensive strategies targeting all reproducibles ensures more efficient termite colony eradication.

Expert Pest Control in Parrish!
Ready to keep your home pest-free? Reach out to Parrish Pest Control at (941) 297-2817 for fast and effective pest management solutions. Serving Parrish, FL, we guarantee a safe, comfortable, and pest-free environment for your home.
Get StartedAgricultural Significance
Termites, known for their wood-feeding habits, can wreak havoc on local agriculture in areas like Parrish. Secondary and tertiary reproductives may contribute to continuous damage if not adequately controlled. Farmers and property owners benefit significantly from knowing these hidden breeders, leading to more targeted and effective termite treatment plans.
By understanding secondary and tertiary reproductives’ roles and characteristics, you become better equipped to handle termite infestations. This knowledge, combined with strategic termite queen treatment, helps curb the growth and spread of these resilient pests.
Queen Termite Lifespan
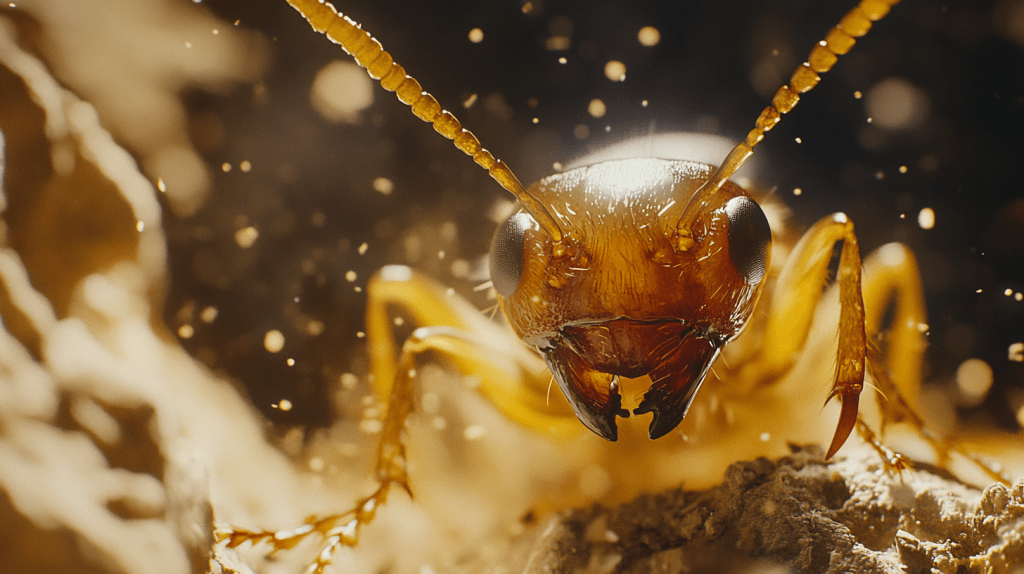

In the termite industry, the queen termite holds a remarkable status, especially in the thriving colonies of Parrish, FL. Her longevity sets her apart from other colony members. While workers and soldiers typically live for just a few months to a couple of years, a queen termite can live up to 15-25 years under optimal conditions. This extended lifespan allows her to lay millions of eggs throughout her life, ensuring the colony’s persistent growth.
The queen’s important lifespan relates to her reproductive role. She is the central figure in termite reproduction, continuously producing offspring and maintaining the colony’s structure. Her swollen abdomen, specifically adapted to maximize egg production, is one of the indicators when identifying a termite queen. Her ability to produce large numbers of termite queen eggs daily supports the infestation challenges in regions like Parrish.
Environmental factors in Parrish, such as humidity and temperature, also influence the queen’s lifespan. The subtropical climate provides ideal conditions for her survival and reproduction. As a termite control expert, understanding these conditions helps tailor effective termite queen treatment strategies. For example, controlling moisture levels around your property can disrupt favorable conditions that support termite colonies.
Eliminating the queen plays a crucial role in controlling termite populations. If you’re wondering how to kill a termite queen, direct methods like bait systems can target her effectively. Once the queen is removed, the colony’s growth halts, and secondary reproductives might take time to mature, providing a window to manage the infestation better.
Recognizing the termite queen’s longevity and its impact on the colony highlights why it’s pivotal to carry out comprehensive termite control measures. In your termite management plan, focus on the queen’s unique vulnerabilities to disrupt the colony’s reproductive cycle efficiently.
Queen Termite Size
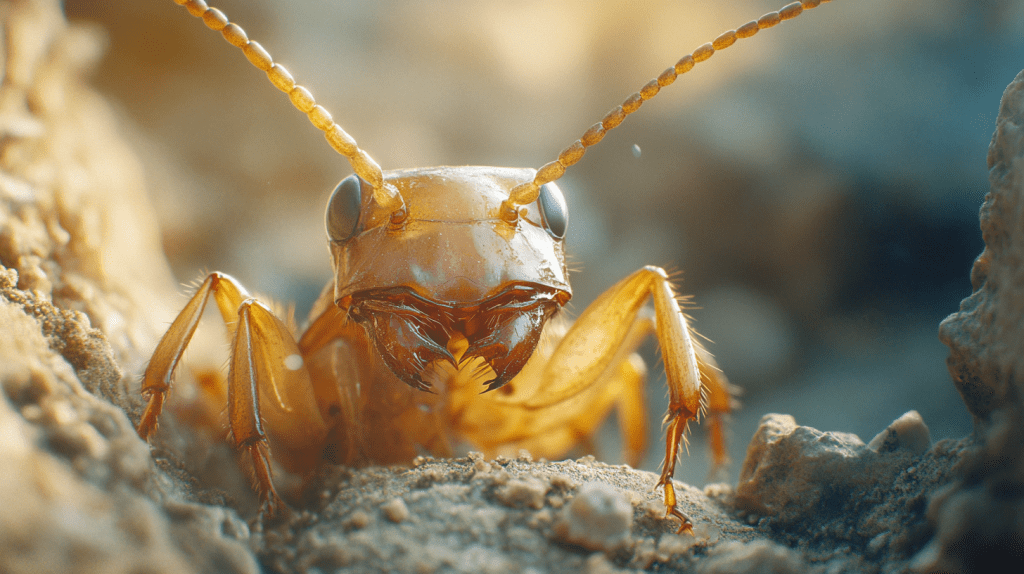
Understanding the pivotal role of the termite queen in colony survival helps you appreciate the complexity of termite management. Her ability to produce thousands of eggs daily makes her a central figure in the colony’s lifecycle. Recognizing her distinct physical characteristics and the influence of her pheromones is crucial for effective pest control.
Identifying secondary and tertiary reproductives adds another layer to your termite management strategies. These backup reproductives can sustain the colony, making it essential to target them as well. Leveraging methods like bait systems can help disrupt the colony’s reproductive cycle, ensuring more effective termite control.
By focusing on the termite queen and her backup reproductives, you can develop comprehensive strategies that protect your property from extensive termite damage. Understanding these aspects will enable you to manage infestations more effectively, safeguarding your property and investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes the termite queen so important in a termite colony?
The termite queen is essential because she lays thousands of eggs daily, ensuring the colony’s survival and growth. Her pheromones also regulate colony activities and reproductive behaviors.
How can the termite queen be identified?
The termite queen can be identified by her large size, about 1.5 to 2 inches long, and her swollen abdomen, which maximizes egg production. She differs from other colony members, like workers and kings, in appearance.
What are secondary and tertiary reproductives in a termite colony?
Secondary and tertiary reproductives are backup egg-layers that take over if the primary queen is damaged or dies. Secondary reproductives resemble larger workers, while tertiary ones look like nymphs with wing buds.
Why is it challenging to control termite colonies?
Controlling termite colonies is difficult because the queen’s prolific egg-laying leads to rapid population growth. Additionally, secondary and tertiary reproductives can sustain the colony if the primary queen is eliminated.
How long can a termite queen live?
A termite queen can live between 15 to 25 years under optimal conditions, laying millions of eggs throughout her life. Her longevity is crucial for the colony’s maintenance and expansion.
What factors influence the lifespan and reproductive capacity of the termite queen?
Environmental factors like humidity and temperature significantly impact the queen’s lifespan and reproductive abilities. The favorable climate of Parrish, FL, supports her prolific egg-laying.
How do termite queens affect pest control strategies?
Termite queens complicate pest control because their egg-laying leads to large infestations. Eliminating the queen disrupts the colony’s reproductive cycle, making it a key target in pest management.
What methods are effective in eliminating the termite queen?
Bait systems are an effective method to eliminate the termite queen. By targeting her, these systems disrupt the reproductive cycle and help manage the termite infestation in the colony.









