Table of Contents
Ever found yourself startled by those long-legged critters skittering across your living room floor? Daddy long legs, with their spindly limbs and almost ghost-like presence, can be quite the unexpected guests. You might’ve even wondered if they’re dangerous or what they’re doing in your home in the first place.
While these arachnids are harmless and actually beneficial predators, their presence indoors can still be unsettling. Imagine enjoying a quiet evening, only to spot one of these creatures dangling from the ceiling. It’s enough to make anyone jump! But don’t worry, there are simple steps you can take to keep them out and maintain your peace of mind. By sealing entry points, reducing moisture, and decluttering your space, you can create an environment that’s less inviting for these eight-legged visitors.
Key Takeaways
- Harmless Creatures: Daddy long legs, belonging to the order Opiliones, are harmless arachnids despite myths about their venom. They pose no threat to humans.
- Beneficial Predators: These arachnids help control pest populations by preying on small, soft-bodied insects, as well as recycling decaying matter.
- Habitat Diversity: Daddy long legs thrive in various environments, from humid forests to urban settings. They are adaptable, living in moist areas but also adjusting to drier climates.
- Unique Defensive Behaviors: They have fascinating defense mechanisms like autotomy (detaching legs to escape predators) and producing chemicals to deter threats.
- Common Misconceptions: The term “daddy long legs” can refer to different creatures, including harvestmen, cellar spiders, and crane flies. Misunderstandings about their venom and species often arise.
- Ecological Importance: Daddy long legs play a vital role in ecosystems by aiding in decomposition and providing food for predators, thus contributing to the balance of natural communities.
Overview of Daddy Long Legs
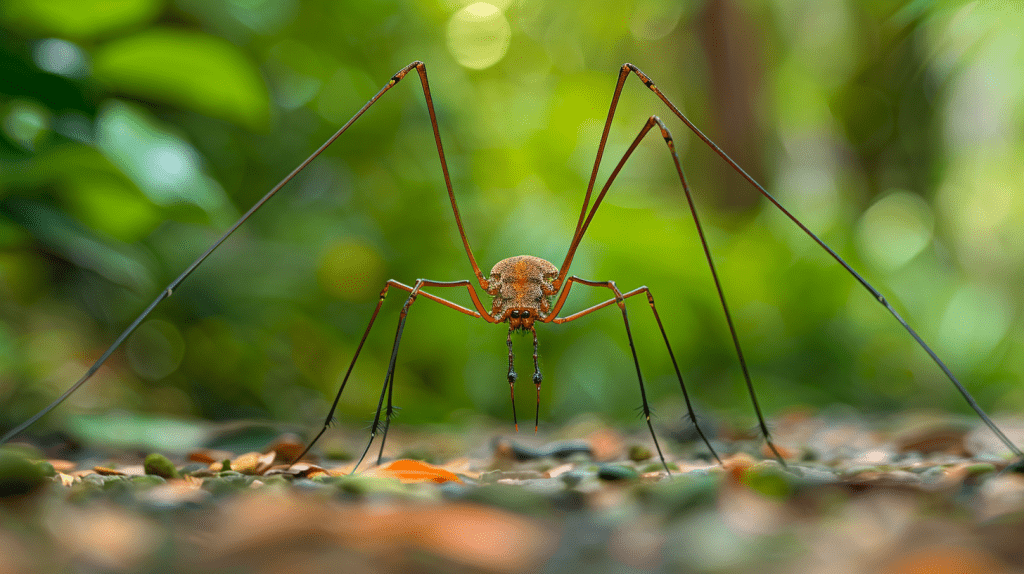

Daddy long legs, or harvestmen, might’ve caught your curiosity while strolling outdoors. These curious creatures belong to the order Opiliones and can be surprisingly fascinating once you know more about them.
Types and Classification
Daddy long legs fall under the order Opiliones within the class Arachnida. There are over 6,000 known species, divided into four suborders: Cyphophthalmi, Dyspnoi, Eupnoi, Laniatores, and the extinct Tetrophthalmi. Each suborder showcases unique traits and adaptations, making them a diverse group. You may not see all types regularly but knowing their classifications helps in understanding their varied habitats and behaviors.
Physical Characteristics
Daddy long legs are easily identifiable by their spherical or ovoid bodies. Even though myths about their venom, they possess none capable of harming humans. Their small body sizes, ranging from 0.04 to 0.35 inches, and long, spindly legs make them look delicate. Interesting, right? These adaptations help them maneuver and escape predators when needed. They thrive in moist environments but can adapt to dry climates as well.
Daddy Long Legs: Identification, Behavior, and Management

Identification
Daddy Long Legs Spiders (*Pholcus phalangioides*)
- Appearance: Recognized by their long, thin legs and small bodies, these spiders are typically pale or light brown with a brown patch on the carapace.
- Size: Up to 1.5 inches (38 mm) in total length, including their legs.
- Webs: Messy, tangled webs often found in corners of rooms, under furniture, or in garages.
Harvestmen (Order Opiliones)
- Appearance: Single, rounded body segment with long legs; does not produce silk or spin webs.
- Size: Smaller than daddy long legs spiders.
- Eyes: Two eyes located on a small bump.
Crane Flies
- Appearance: Resembling large mosquitoes, crane flies have long legs and wings; they are insects, not arachnids.
- Size: Larger than both daddy long legs spiders and harvestmen.
Habitat
- Daddy Long Legs Spiders: Commonly found in urban areas, especially in homes, where they prefer warm environments such as attics, basements, and corners of rooms.
- Harvestmen: Typically found outdoors in moist habitats under rocks, logs, or leaf litter.
- Crane Flies: Often found near water sources or damp areas.
Behavior
- Feeding Habits:
- Defense Mechanisms:
- Daddy Long Legs Spiders: Vibrate their webs to deter predators.
- Harvestmen: Emit foul-smelling secretions from glands when threatened.
Health Risks
- Venomous Myths: The myth that daddy long legs spiders are among the most venomous but cannot bite humans is false. Their venom is not harmful to humans, and they are considered harmless.
- Bites: If bitten by a daddy long legs spider, the reaction is usually minimal—a slight stinging sensation without serious consequences.
Management and Control
Prevention
- Cleanliness: Maintain a clean home, removing clutter where spiders may hide.
- Seal Entry Points: Seal cracks and gaps around windows and doors to prevent spiders from entering.
Treatment Options
- Vacuuming: Remove webs and spiders using a vacuum cleaner.
- Insecticides: Apply carefully to minimize harm to beneficial species.
Understanding the distinctions between daddy long legs spiders, harvestmen, and crane flies is essential for proper identification and management. Daddy long legs spiders are harmless to humans, and implementing preventive measures can help manage their presence effectively.
Understanding their unique physical attributes and classifications gives you a better appreciation of these misunderstood creatures. Rather than seeing them as eerie invaders, you’ll find them fascinating additions to the ecosystem.
Habitat and Distribution
Daddy long legs, also known as harvestmen, inhabit various environments worldwide. These intriguing creatures can be found in both natural and urban settings, making them a fascinating subject for exploration.
Where They Live
Daddy long legs live in many different areas across the globe. You’ll find them in forests and caves, exploring through leaf litter on the forest floor or climbing on rocks and vegetation. Some species even make their homes in urban environments, lurking in crawl spaces and under eaves, especially during warm months. It’s common to spot them grouping together in moist, dark areas to retain water. Isn’t it fascinating how they adapt to diverse habitats?

Expert Spider Control in Parrish!
Ready to keep your home spider-free? Reach out to Parrish Pest Control at (941) 297-2817 for fast and effective spider management solutions. Serving Parrish, FL, we guarantee a safe, comfortable, and spider-free environment for your home.
Get StartedEnvironmental Preferences
Daddy long legs prefer humid or moist habitats. Forests, caves, and wetlands are their primary domains. Certain species have adapted to drier environments, showcasing their incredible versatility. In urban areas, they often hide in buildings, particularly in damp, shaded spots. This adaptability highlights their survival skills, making them resilient in varying conditions.
Their presence in both temperate and tropical climates demonstrates their global reach. For example, Missouri cave dwellers gather in dark, wet places near cave entrances. In more arid regions, they use their long legs to travel across the ground, showing a fascinating adaptability to diverse environments.
Understanding these aspects of daddy long legs’ habitats and distributions not only showcases their versatility but also their importance in the ecosystem. You’ll find them in surprising places, each time showcasing their unique ability to thrive.
Behavior and Diet

Ever wondered what life looks like for daddy long legs, or harvestmen? It’s quite fascinating! These arachnids lead lives that are rich in survival tactics and dietary adaptability.
Feeding Habits
Daddy long legs have diverse diets that reflect their opportunistic nature. They prey on small, soft-bodied insects, providing a natural pest control service. Dead insects, rotting fruit, mushrooms, and even animal droppings are consumed as part of their scavenging activities. When the chance arises, they catch small insects and other prey. This varied diet ensures they play a crucial role in the ecosystem, helping to recycle decaying matter.
Common Behaviors
Daddy long legs display unique behaviors that ensure their survival. Their long legs are versatile tools used for crawling, climbing, and even walking on water. Imagine being able to use your legs to sense your surroundings and escape danger by detaching them when threatened! Yes, they can do that through a process called autotomy, where the detached leg continues to twitch, confusing predators long enough for the daddy long legs to escape. Also, they have glands that produce chemicals like phenols, quinones, ketones, or alcohols to repel potential threats.
In understanding these behaviors and feeding habits, you gain insight into their vital role in nature. Daddy long legs are not just harmless to humans but are also incredible at maintaining the balance in ecosystems.
Common Misconceptions

When thinking about daddy long legs, a mix of myths and mix-ups often comes to mind. It’s time to set the record straight and help you understand these fascinating creatures better.
Myth of Venom Toxicity
Many people believe that daddy long legs hold the title for the most venomous spiders, but in reality, this is far from the truth. Have you heard that their fangs are too short to penetrate human skin? This myth paints a misleading picture. Cellar spiders, often called daddy long legs, indeed produce venom, but it’s mild and not harmful to humans. In fact, the MythBusters team tested this myth, showing that their venom had little effect even on the smallest of creatures. So, if you come across a cellar spider, there’s no need to worry about a deadly bite.
Misidentified Species
The term “daddy long legs” can be confusing, as it refers to different creatures. Did you know that not all daddy long legs are spiders? Let’s break it down. Harvestmen are arachnids often mistaken for spiders, but they lack venom, fangs, and silk glands. Plus, they have a single body segment and only two eyes. Then, we have cellar spiders, which are true spiders. They do produce venom but only enough to give a mild sting. Finally, crane flies are insects sometimes called daddy long legs. They can’t bite since they don’t have a mouth.
Clearing these misconceptions helps appreciate the truth about daddy long legs and their harmless nature.
Ecological Importance
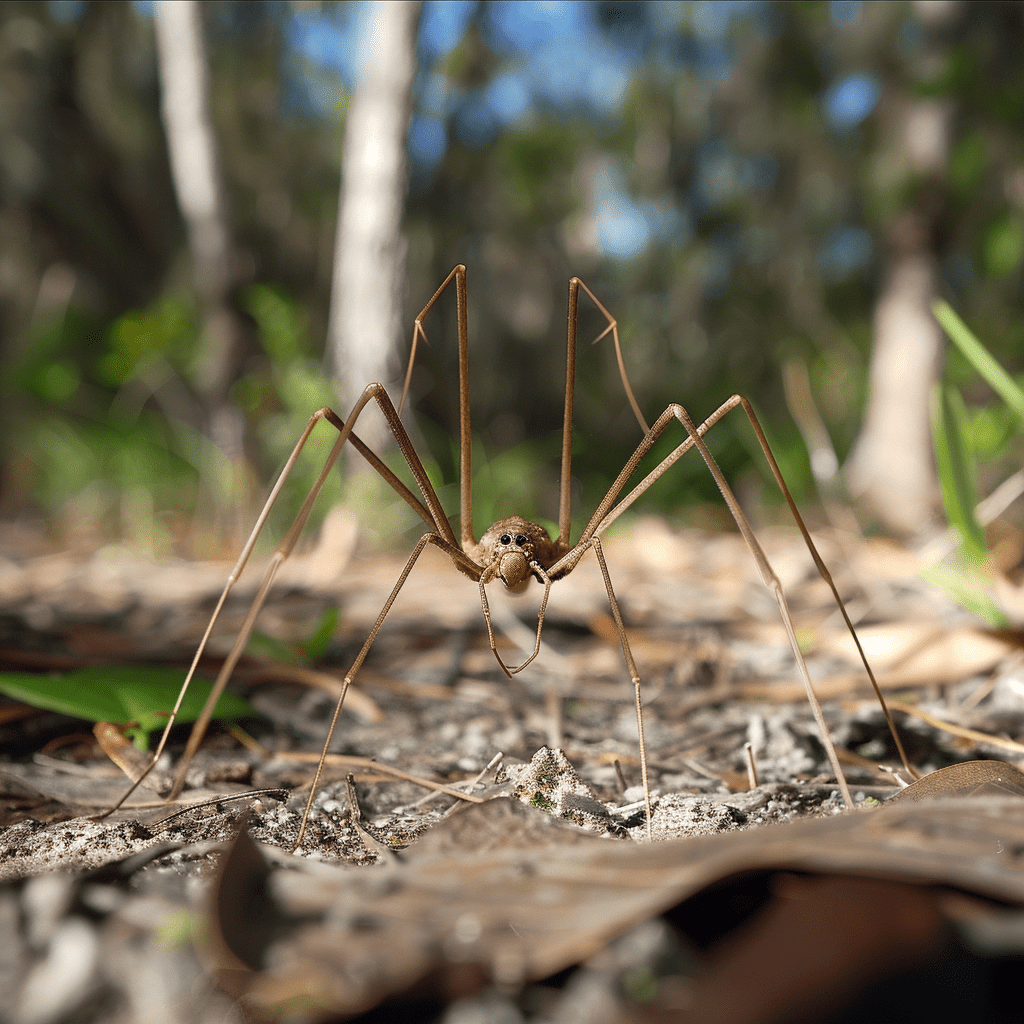

Daddy long legs, or harvestmen, may look delicate, but they play a big role in our ecosystems. Their presence in gardens, forests, and fields brings several benefits that you might not expect.
Role in Ecosystem
Daddy long legs clean up the environment by consuming dead insects and organic debris. Imagine a garden littered with decaying matter. These creatures help break it down, accelerating decomposition and nutrient recycling. Their work as scavengers ensures the soil remains fertile, promoting healthier plant growth.
Plus, as omnivores, daddy long legs control populations of small insects, including pests like aphids. Consider the impact on agriculture: fewer aphids mean healthier crops and reduced dependency on chemical pesticides. Farmers indirectly benefit from the presence of daddy long legs, which maintain the balance of pest populations naturally.
Daddy long legs also form a crucial part of the food web. Birds, lizards, and other predators rely on them as a food source. This interconnected relationship underscores their importance. Without these creatures, many predator species might struggle to find enough food, causing disruptions in the ecosystem.
Interaction with Other Species
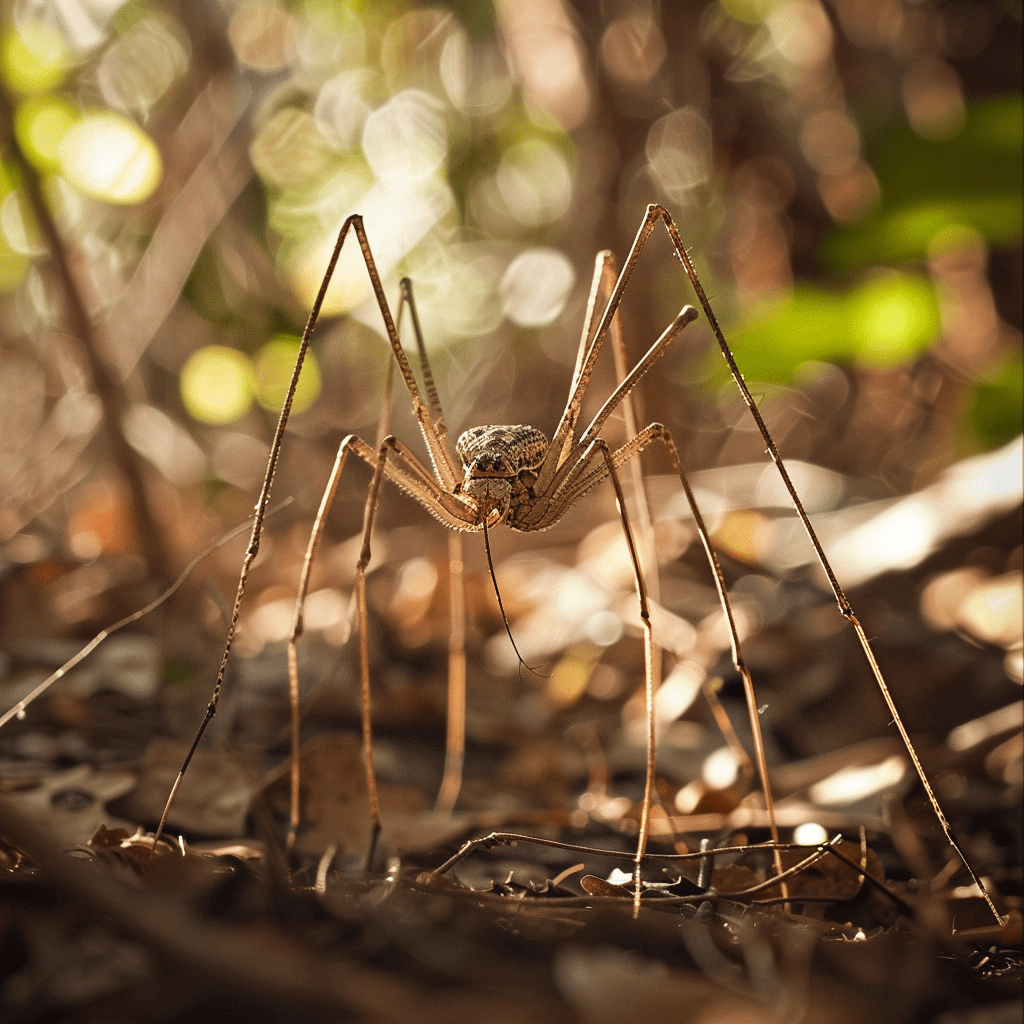

Interactions between daddy long legs and other species are subtle but significant. For example, their predation on aphids directly benefits gardeners and farmers. If you’ve ever dealt with an aphid infestation, you’d appreciate these natural pest controllers. Their diet also includes small insects and fungi, reducing the spread of plant diseases.
Daddy long legs are relatively defenseless when faced with their predators. Birds and lizards frequently hunt them for food, making them an essential link in the energy transfer within ecosystems. This predatory pressure ensures that daddy long legs populations are kept in check, preventing them from becoming too numerous and overwhelming their habitats.
Through these interactions, daddy long legs maintain balance in natural communities, supporting both plant and animal life. Their ecological role, while often overlooked, is indispensable for the health of many ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What attracts daddy long legs?
They are usually found outdoors and near outdoor lights because the lights attract insects, providing an abundant food source. To reduce their presence, minimize outdoor lighting at night and use a broom to move them away from entry points.
Is a daddy long legs a spider or crane fly?
Daddy long legs, or harvestmen, belong to the order Opiliones in the class Arachnida and are distinct from spiders and crane flies. They have unique features and do not spin webs or produce silk like spiders.
What is special about Daddy Long Legs?
Daddy long legs are unique as they don’t spin webs or produce venom. They have only two eyes, unlike spiders, and play a significant ecological role in decomposing organic matter and controlling pest populations.
Can daddy long legs see you?
Daddy long legs have simple eyes that act as light sensors and provide only blurry images. Their vision is not very effective for detailed viewing, so they likely can’t see you clearly.
Why do daddy long legs clump together?
Daddy long legs may cluster together to ward off predators since they lack venom or web-spinning abilities. When in groups, they can release a stinky secretion that is more effective in deterring threats.






